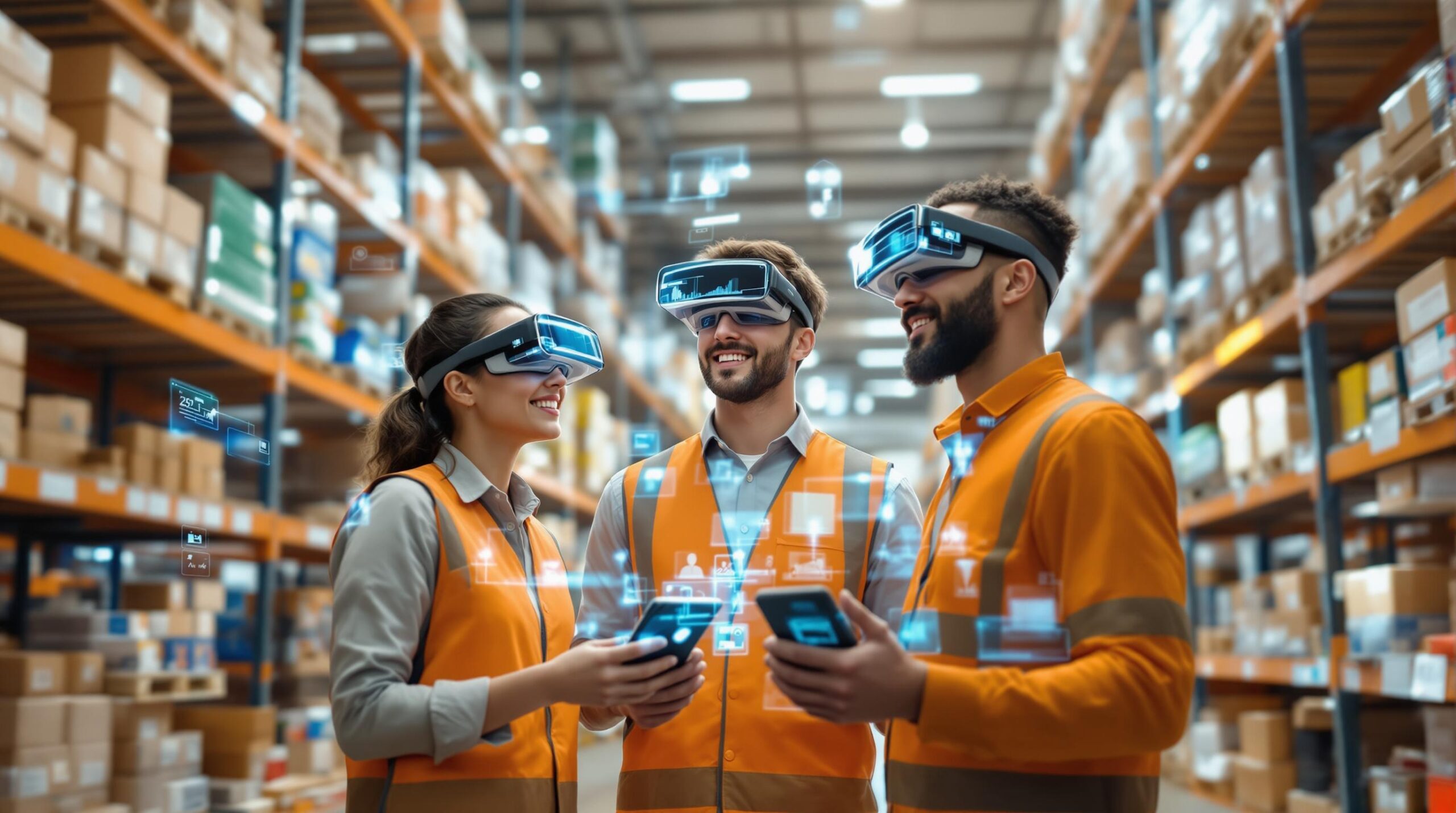
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming logistics by improving efficiency, accuracy, and training processes. Companies like DHL and Walmart are already leveraging AR for tasks like warehouse picking, inventory tracking, and route optimization. Here’s what AR is doing for logistics:
- Warehouse Picking: AR devices like Microsoft HoloLens guide workers, reducing errors by 25-40%.
- Inventory Tracking: Real-time stock updates using AR and IoT sensors.
- Route Optimization: AI-integrated AR reduces CO₂ emissions and improves delivery efficiency.
- Training: AR-based programs cut onboarding time by 30-40%.
- Equipment Repairs: Hands-free AR tools speed up maintenance by 45%.
With tools like Vuzix smart glasses and platforms like TeamViewer, AR is reshaping logistics operations while integrating with systems like SAP EWM. The future combines AR with AI and 5G for even smarter, faster workflows.
Vision Picking at DHL – Augmented Reality in Logistics
5 Main AR Applications in Logistics
Smart Warehouse Picking
AR-powered picking systems have changed how warehouses operate by offering precise digital guidance. Using devices like Microsoft HoloLens, which utilize spatial mapping technology (SLAM), these systems overlay digital markers on physical items. This eliminates guesswork, reduces errors, and improves efficiency. Plus, it works seamlessly with real-time inventory management systems.
Live Inventory Tracking
AR has made stock control much more efficient by enabling real-time inventory tracking. By combining RFID and IoT sensors with AR displays, teams can visually verify inventory movements instantly and keep tabs on stock levels [2][6].
"AR gives teams hands-free access to operational data during workflows." – Jan-Willem De Jong, DHL Supply Chain Director [11]
Route Planning and Navigation
AR isn’t just for warehouses – it’s also reshaping larger supply chain operations. Take Walmart Commerce Technologies as an example. Their AI-powered Route Optimization system integrates live traffic, weather updates, warehouse layouts, and AI-driven adjustments. The result? A 15% reduction in empty trailer miles and a massive cut of 94 million pounds in CO² emissions annually [10].
Staff Training Programs
Training programs using AR have made onboarding faster and improved safety compliance. For instance, Johnson & Johnson Vision Care uses holographic guides to teach proper equipment handling. This approach has cut onboarding time by 30% [6].
Equipment Repairs and Support
AR also plays a big role in equipment repairs, making the process quicker and more efficient. GE Healthcare, for example, uses HoloLens-guided maintenance, which has reduced repair downtime by 45% [4].
Some standout features include:
- Live collaboration with experts via AR feeds
- Digital assembly guides for faster repairs
- Hands-free access to schematics
Platforms like TeamViewer Frontline allow technicians to share real-time AR feeds with remote specialists, while Vuzix M400 smart glasses provide hands-free access to technical documentation during repairs [4][8].
AR Setup Requirements
Hardware and Software Selection
Choosing the right hardware and software is crucial for implementing AR in logistics. Devices like Microsoft HoloLens 2 and Google Glass Enterprise Edition are popular in warehouses due to their hands-free design and durability.
Here are some key hardware specifications to consider for warehouse environments:
| Key Requirements | Minimum Spec | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Life | 8+ hours | Supports full-shift operations |
| Field of View | >50° vertical | Aligns with storage rack heights |
| Durability | IP-rated protection | Handles tough warehouse conditions |
| Integration | WMS compatibility | Works with existing systems |
Platforms such as META-aivi help reduce counting errors by up to 40%, integrating seamlessly with systems like SAP EWM [4][9].
Security and Data Protection
When AR systems handle sensitive data, robust security measures are a must. This includes AES-256 encryption and compliance with GDPR for managing data, especially in IoT setups.
"AR implementations must anonymize biometric data collected through eye-tracking sensors (used in Geodis’ training systems) and implement clear consent protocols for performance monitoring features" – Geodis Training Systems Documentation [7]
Companies like Sidekick Interactive specialize in high-level encryption for IoT devices and secure API connections, ensuring data is protected at every step.
Common Issues and Fixes
One of the biggest hurdles in AR adoption is getting employees on board. A phased approach works best:
- Start with 6-8 week trials for basic tasks.
- Gradually expand to advanced features over an 18-month period [1].
For managing systems across multiple locations, centralized platforms like Zebra’s Savanna are invaluable. They allow remote updates and patches, ensuring smooth operations globally [2]. Geodis highlights the importance of customizing AR systems, using tailored UI profiles for different environments like ambient and cold storage facilities to meet specific needs [1][12].
sbb-itb-7af2948
Future AR Developments
AI and AR Combined
AI is adding new dimensions to AR, making it even more powerful for logistics:
- NeuroSYS’s AI-AR system: By using real-time weather data, this system optimizes maritime routes, cutting fuel consumption by 12-18% [3][5].
- Warehouse operations: AI-powered AR visors are speeding up cycle counts by 30-40%, making inventory management more efficient [4][6].
- 5G and AR in transportation: Verizon’s tests show that 5G-enabled AR route planning reduces system latency to under 10ms. This allows truck drivers to see real-time port congestion data directly on their windshields [3].
New AR Device Types
AR devices tailored for warehouses are addressing specific industrial challenges. Here’s a quick look:
| Device Type | Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Third Wave HMT-1Z1 | Counterbalanced design | Reduces abandonment rates by 65% [6] |
| Vuzix M4000 | Thermal imaging | Improves inventory monitoring [4] |
| Panasonic Toughbook A3 | Cold chain sensors | Enables real-time temperature tracking [2] |
Some companies are taking a different approach. LightGuide Systems, for example, uses overhead AR projectors to show floor waypoints. This eliminates the need for wearables altogether [2].
Security is also a top priority in next-gen AR logistics. Companies like Sidekick Interactive are stepping up with solutions like end-to-end encryption and biometric authentication at the device level. These features are especially critical in industries like pharmaceuticals, where sensitive shipment data must be protected. Their zero-trust architecture ensures only authorized users can access AR interfaces.
On top of operational improvements, AR is contributing to eco-friendly practices. For instance, DB Schenker’s AI-enhanced AR navigation tools have helped achieve a 15% cut in CO2 emissions by optimizing delivery routes [3][5].
Conclusion
Key Highlights
AR is making a noticeable impact in logistics, with companies like Maersk achieving a 15% improvement in space usage through AR-driven packing simulations, and Geodis cutting training times by 40%. These examples show how AR extends its benefits well beyond just improving efficiency.
Choosing the Right Development Partners
As AR technology advances, selecting the right development partners becomes essential to staying ahead. Companies like Sidekick Interactive stand out by offering military-grade encryption for security and expertise in integrating with warehouse management systems (WMS), setting them apart from simpler low-code options.
The future success of AR in logistics hinges on how well it integrates with other advancing technologies. Development partners should offer ongoing support for updates and maintenance, including:
- Future-Ready Features: AI integration for smarter routing solutions.
Look for partners who deeply understand the technical and operational challenges of logistics. This ensures AR solutions evolve alongside advancements like AI-powered routing and 5G connectivity.
FAQs
What does AR mean in logistics?
Augmented Reality (AR) in logistics adds digital overlays to the physical environment, helping improve processes and workflows.
Here’s how AR is being used:
- Warehouse Operations: AR-guided picking systems offer real-time visual cues, making order fulfillment faster and more accurate.
- Navigation Tools: AR can project optimized routes directly onto drivers’ windshields, improving delivery efficiency [5].
- Training Programs: DHL demonstrated that AR-based training can boost task retention by 70% compared to traditional video-based methods [7].
To successfully use AR in logistics, you’ll need:
- Strong security encryption
- Integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
- Reliable and durable hardware
For more details, refer to the Security and Data Protection section mentioned earlier.