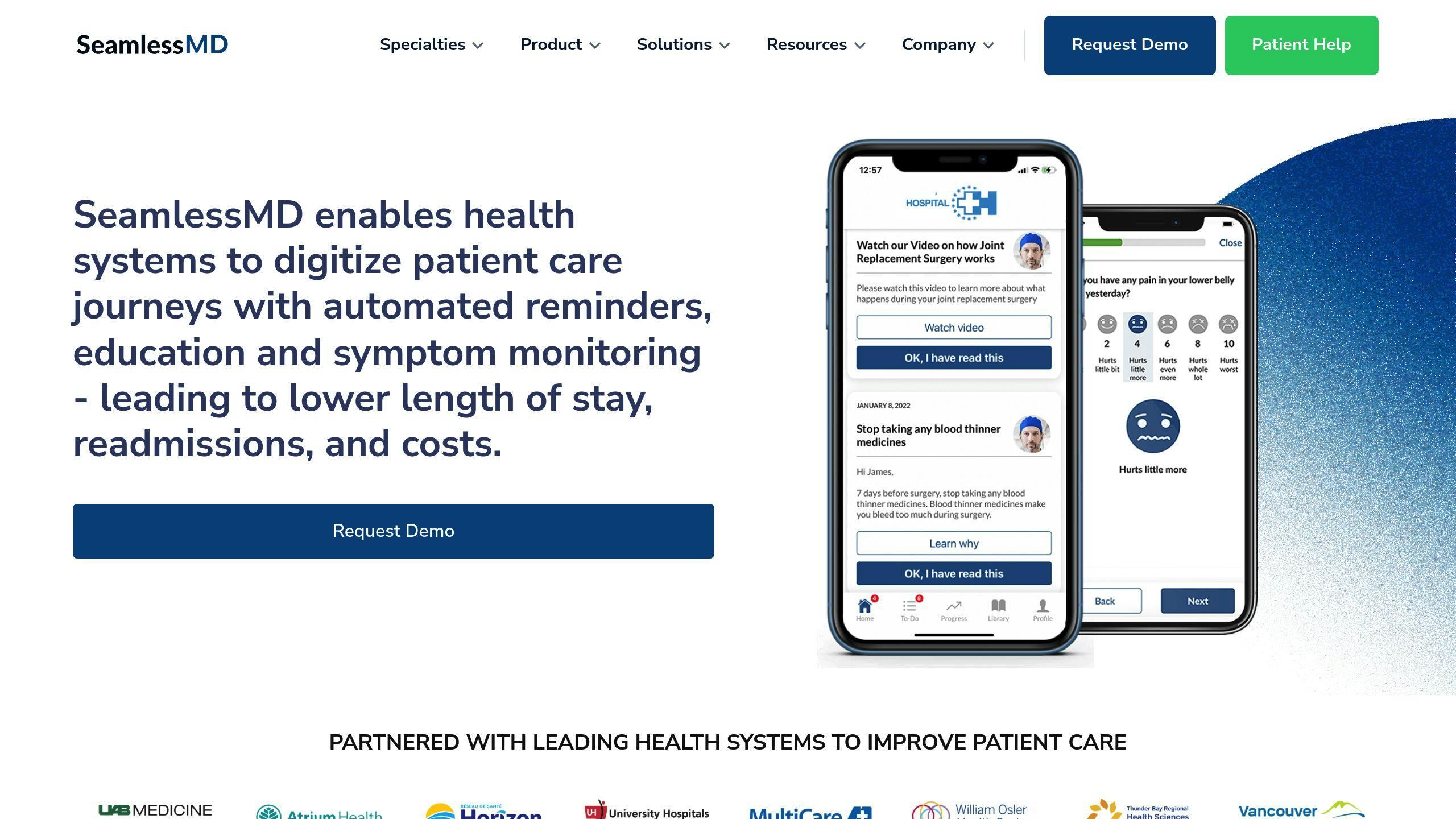
Patient engagement apps are transforming healthcare by improving communication, simplifying processes, and empowering patients to manage their health. They offer features like secure messaging, appointment scheduling, and remote health monitoring. These tools not only enhance patient-provider connections but also help manage chronic conditions and improve outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
- What They Are: Apps that connect patients with healthcare providers for better communication and health management.
- Why They Matter: They improve care, reduce administrative work, and provide tools for chronic condition management.
- Key Features:
- Secure Messaging: HIPAA-compliant communication for privacy.
- Scheduling: Easy appointment booking and reminders.
- Remote Monitoring: IoT integration for real-time health tracking.
- Advanced Tech:
- Blockchain: For secure, tamper-proof data sharing.
- Augmented Reality (AR): For interactive health education.
- Data Analytics: To personalize care and identify risks.
By focusing on user-friendly design, strong security, and reliable performance, these apps are shaping the future of healthcare with personalized, accessible, and efficient solutions.
How The SeamlessMD Patient Engagement App Works
Key Features of Patient Engagement Apps
Patient engagement apps succeed by addressing patient needs and simplifying healthcare processes. Here’s how they do it:
Secure Messaging and Communication
Handling sensitive health information demands top-notch security. These apps must include encrypted messaging systems that align with HIPAA regulations. For instance, Medtronic’s CareLink platform ensures privacy by encrypting health data and adhering to strict privacy standards [1].
Key benefits of secure messaging include:
- Confidential communication between patients and providers, including secure document sharing.
- Timely updates such as lab results, treatment plans, and prescription refill notifications.
Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Streamlining appointment management helps both patients and healthcare providers. Features like real-time availability, automated reminders to cut down no-shows, waitlist management to optimize scheduling, and easy rescheduling options make the process smoother for everyone.
Remote Monitoring and IoT Integration
The integration of IoT has changed the game for remote health monitoring. Philips’ HealthSuite, for example, connects various health devices to provide a more complete view of patient health [1].
These systems enable:
- Real-time tracking of vital signs and health metrics.
- Better management of chronic conditions.
- Early identification of potential health issues, paving the way for timely care.
To make IoT work effectively, apps need to ensure robust data security, privacy safeguards, and seamless device connectivity. This creates a reliable system for both routine monitoring and managing more complex health conditions [2].
Each of these features plays a critical role in building a patient engagement app that meets user needs while maintaining high standards of privacy and usability.
Best Practices for Design and Development
User-Friendly UX/UI Design
When building patient engagement apps, focusing on an easy-to-use and functional interface is key. This involves clear typography, consistent color schemes, and logical navigation. In healthcare, where users may have different levels of tech experience or physical challenges, designing with empathy is especially important [2].
Key features of effective UX/UI design include intuitive navigation, accessibility tools like text-to-speech and adjustable font sizes, and personalized dashboards. These elements make the app more inclusive and enjoyable to use. However, while improving usability is important, ensuring the app complies with healthcare regulations is just as critical.
Meeting Healthcare Standards
To meet healthcare standards, apps need strong encryption, secure user authentication, and full compliance with HIPAA guidelines. These measures protect patient data while maintaining ease of use. As mentioned in the ‘Secure Messaging’ section, HIPAA compliance combined with robust encryption is non-negotiable for safeguarding sensitive information.
Iterative Development and Testing
Using an iterative development process – starting with prototypes, gathering feedback, and refining through testing – helps create an app that meets user needs and regulatory requirements. This method not only improves functionality but also builds user trust by delivering a reliable product.
During development, constant feedback and updates are crucial, especially for core features like appointment scheduling and secure messaging. Testing with varied user groups, including patients, healthcare providers, and caregivers, ensures the app serves its purpose effectively while staying compliant with healthcare standards.
sbb-itb-7af2948
Using Advanced Technology in Patient Engagement Apps
Today’s patient engagement apps are reshaping healthcare by using advanced technologies to improve how patients and providers connect and manage care. These tools are redefining the patient experience and boosting health outcomes.
Blockchain for Secure Data Sharing
Blockchain technology offers a secure way to record and share patient data. It ensures information is tamper-proof while allowing controlled access to authorized users. For example, Medibloc provides a platform where patients decide who can access their medical data and how it’s shared [3]. By using blockchain, these apps not only protect sensitive information but also build patient confidence, which is key to widespread adoption.
Augmented Reality for Health Education
Augmented Reality (AR) is changing how patients learn about their health. Through interactive visuals, AR simplifies complex medical information, making it easier for patients to grasp their conditions and treatments.
"Augmented reality can be a game-changer in healthcare education, enabling patients to better understand their conditions and treatments in an engaging and interactive way." – Dr. Brennan Spiegel, Director of Health Services Research, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
AR applications include 3D models that help patients understand anatomy, virtual tools for managing medications, and treatment simulations to prepare for medical procedures. While AR offers exciting possibilities, its implementation requires careful planning to meet healthcare regulations and ensure smooth integration.
Advanced Technology Integration
Building apps with advanced features demands both technical know-how and an understanding of healthcare regulations. Companies like Sidekick Interactive specialize in creating secure apps that incorporate technologies like blockchain, AR, and IoT. Their expertise ensures these tools are not only functional but also meet strict compliance and usability standards.
Some standout features include:
- Secure blockchain systems for protecting patient data
- AR-based tools for interactive health education
- IoT compatibility for remote health monitoring
- 3D visualization tools to enhance medical imaging
These technologies, when combined thoughtfully, create apps that are both powerful and user-friendly, meeting the evolving needs of patients and providers alike.
Challenges in Designing Patient Engagement Apps
Creating patient engagement apps comes with hurdles like adoption, data security, and maintaining performance. Tackling these issues is essential for building healthcare apps that patients trust and use effectively.
Encouraging User Adoption
Getting patients to use an app often boils down to simplifying the experience and showing clear benefits. Many users feel overwhelmed by complicated designs or don’t see the value in engaging.
Key strategies include:
- Streamlined onboarding to guide users from the start.
- Designing for inclusivity, ensuring the app works well for all age groups and technical skill levels.
- Personalized features that offer actionable, relevant insights.
Empathy-driven design helps address users’ psychological and physical needs. While simplicity and usability are important for adoption, securing users’ trust through strong data protection is just as critical.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
With around 70% of healthcare organizations reporting data breaches [1], protecting sensitive medical information is non-negotiable. A multi-layered approach to security is essential.
| Security Layer | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Protect data at all stages | End-to-end encryption for communications |
| Access Control | Manage user permissions | Multi-factor authentication, role-based access |
| Compliance | Meet legal standards | Infrastructure adhering to HIPAA protocols |
| Audit Trails | Monitor data access | Detailed logs of all activities |
Technologies like blockchain can add an extra layer of security by making records tamper-proof and regulating access. However, even the most secure app must perform well to keep users engaged.
Balancing Features and Performance
Striking the right balance between functionality and performance is crucial. Overloading an app with features can lead to sluggish performance, frustrating users.
Here’s how to maintain that balance:
- Focus on core functions like scheduling and messaging before adding extras.
- Conduct rigorous performance tests to ensure the app runs smoothly in different scenarios.
- Use user feedback to refine features and prioritize what matters most.
Accessibility tools, such as font size adjustments, voice commands, and text-to-speech, should also be integrated thoughtfully to cater to all users without slowing down the app [1][2]. Collaborating with experienced developers ensures that advanced features are implemented efficiently while staying compliant with healthcare standards.
Conclusion and Future of Patient Engagement Apps
Key Points to Remember
Patient engagement apps have grown from basic scheduling tools into platforms that help manage various aspects of healthcare. Their success hinges on three main factors: easy-to-use design that encourages people to adopt them, strong security to safeguard sensitive information, and reliable performance for consistent functionality. Together, these features create tools that benefit both patients and healthcare providers while staying compliant with industry regulations.
What’s Next for Patient Engagement Apps?
Patient engagement technology is quickly advancing, shaped by new tech and shifting healthcare demands. Artificial intelligence (AI) is taking center stage, offering personalized healthcare advice and analyzing patient data to deliver tailored care plans. Integration with wearable devices is becoming key for real-time health tracking, helping providers monitor vital signs and activity trends continuously.
On top of that, augmented reality (AR) is changing how people learn about health by turning complex medical ideas into interactive, easy-to-understand visual experiences. As these technologies improve, their combination will lead to even more effective healthcare tools.
Companies like Sidekick Interactive are already using AI and AR to design secure, intuitive, and forward-thinking patient engagement solutions. By blending cutting-edge technology with strong security and simple design, they’re helping healthcare providers adapt to the next generation of digital health tools.
This mix of technologies is reshaping healthcare, paving the way for more personalized, proactive, and accessible care. As these tools continue to develop, they’ll play a bigger role in improving both patient experiences and health outcomes.